Understanding Virtualization
Apr 28th 2025
What is Server Virtualization?
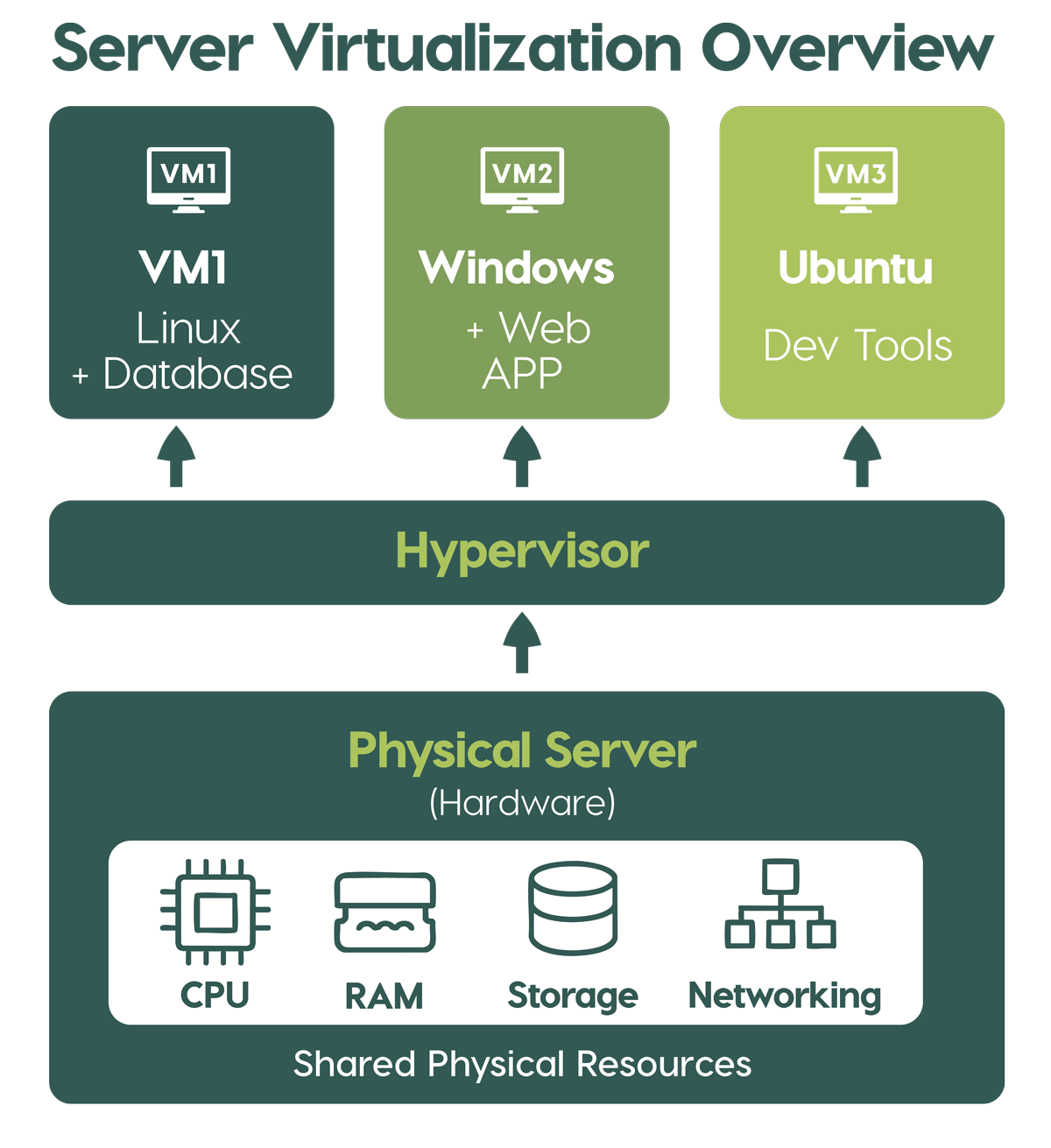
Server virtualization is when you create multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server using software known as a hypervisor. Each virtual machine (VM) operates independently, running its own operating system and applications, as if it were a separate machine. This technology maximizes hardware efficiency by dividing up the server’s resources — CPU, memory, storage, and networking — among multiple virtual environments. Server virtualization enables businesses to optimize IT resources, reduce costs, and scale seamlessly to meet dynamic workload demands. It also allows running multiple operating systems independently on one physical server, improving utilization and reducing carbon footprint.
Think of it like renting out rooms in a house. The physical server is the house, and each virtual machine (VM) is a room with its own purpose, isolated from the others, yet all sharing the same foundation and hardware. Virtualization allows businesses to consolidate workloads, reduce hardware costs, and improve scalability.
Who Uses Server Virtualization?
Virtualization is widely used across industries and many different sizes of operations. Here’s who benefits most:
- Small Businesses: Startups and small enterprises use virtualization to run multiple different services and applications like web servers, email servers, and database servers all on one machine, saving on both hardware and energy costs.
- Medium to Large Enterprises: Larger organizations deploy virtual machines for data centers, cloud computing, and disaster recovery, enabling rapid scaling and efficient resource allocation.
- Developers and IT Professionals: Programmers and sysadmins use virtual machines for testing software in isolated environments or simulating complex setups.
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs): MSPs leverage virtualization to host client services securely and cost-effectively on shared infrastructure.
If you’re running a business with limited IT resources or managing a high-demand data center, virtualization is likely already on your radar.
Virtualization benefits businesses by enabling more efficient resource provisioning and improving IT productivity through faster server provisioning and decommissioning. Servers often run at only 15% to 25% utilization. Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines to share a single physical server’s resources, significantly increasing utilization and reducing idle hardware.
How to Use Server Virtualization
Setting up a virtualized server environment involves a few key steps:
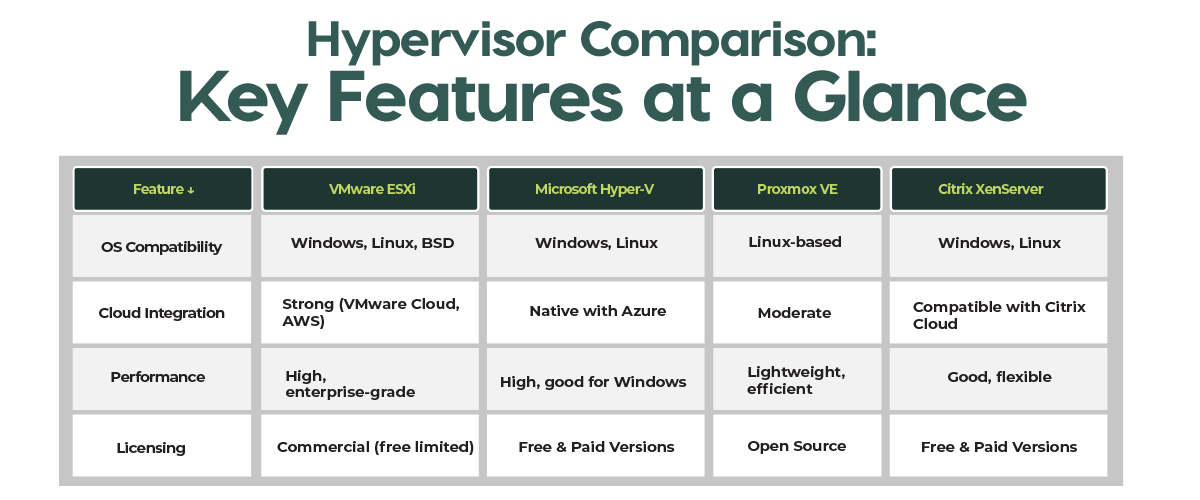
- Choose a Hypervisor: Select a virtualization platform like VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, Proxmox VE, or Citrix XenServer. Each has its strengths — VMware is enterprise-grade, Hyper-V integrates well with Windows, and Proxmox is open-source and budget-friendly. Selecting servers certified for platforms like VMware ESXi, Oracle Linux, and XenServer ensures compatibility and optimized performance.
- Assess Hardware Needs: Ensure your server has sufficient CPU cores, RAM, and storage to handle multiple VMs.
- Install the Hypervisor: Deploy the hypervisor directly on the server hardware (Type 1) or as software on an existing OS (Type 2 — less common for production environments).
- Create Virtual Machines: Allocate resources to each VM based on its workload (e.g., database servers might prioritize RAM, while web servers prioritize CPU).
- Configure Networking: Set up virtual switches to manage communication between VMs and external networks.
- Monitor and Maintain: Use hypervisor tools to track performance, balance resources, and ensure uptime.
For beginners, starting with a user-friendly hypervisor like Proxmox or VMware’s free ESXi version is a good move. Advanced users may integrate automation tools like Ansible or Kubernetes for managing large-scale virtual environments.
Key Specs for Virtualization
Not all servers are created equal for virtualization. Here’s what matters most:
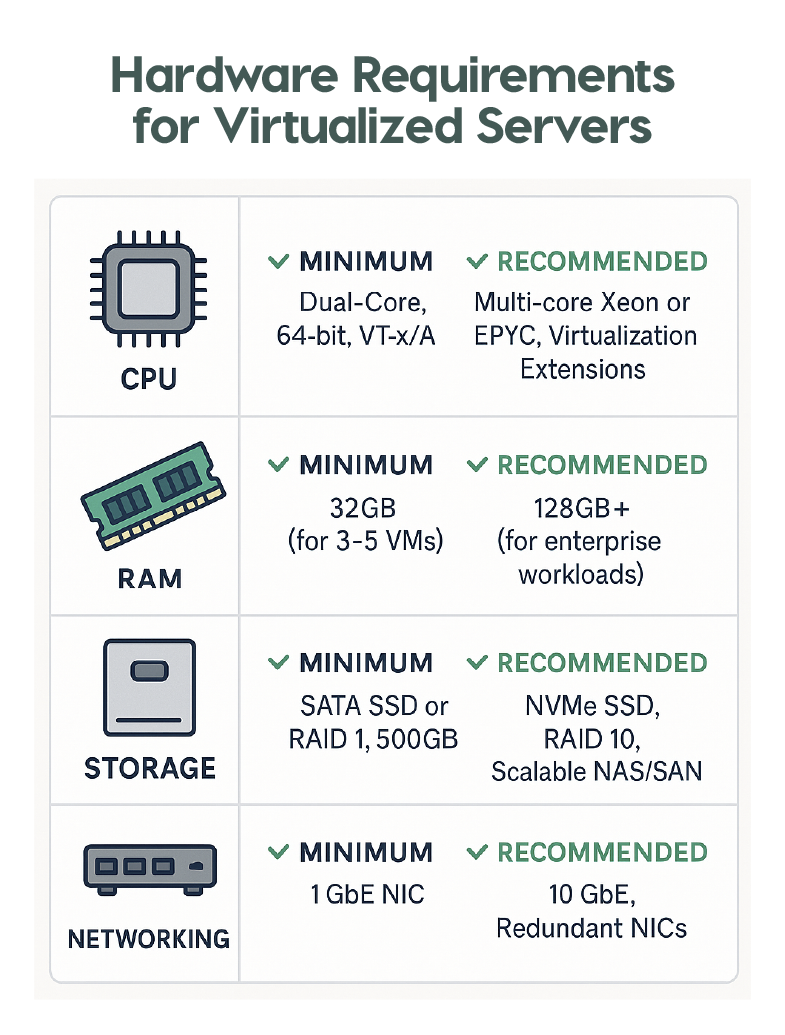
- CPU: Multi-core processors with support for virtualization extensions (Intel VT-x or AMD-V) are critical. More cores and threads allow you to run more VMs simultaneously. Look for modern Xeon or EPYC processors for optimal performance.
- RAM: Memory is often the bottleneck. Plan for 4GB–16GB per VM depending on workload, plus overhead for the hypervisor. 32GB is a bare minimum for small setups; 128GB+ is common for enterprise use.
- Storage: Fast storage like NVMe SSDs or enterprise-grade SATA SSDs improves VM performance. RAID (e.g., RAID 10) adds redundancy. Consider scalable options like NAS or SAN for large deployments.
- Networking: Gigabit or 10GbE network interfaces ensure smooth communication between VMs and clients. Redundant NICs minimize downtime.
- Expandability: Servers with multiple CPU sockets, RAM slots, and PCIe lanes let you grow as your virtualization needs increase.
Popular hypervisors include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, Proxmox VE, and Citrix XenServer, each offering unique advantages like enterprise-grade features or integration with Windows environments.
Good rule of thumb: Overspec slightly to avoid running out of hardware. Running too many VMs on limited resources results in performance bottlenecks and frustrated users. Modern virtualization requires 64-bit multi-core processors with hardware virtualization support, a minimum of 2 GB RAM (though realistically much more), and fast storage. Dual-core CPUs or multiple CPUs are recommended for hosting several VMs.
Conclusion
Selecting the right hardware for server virtualization can significantly impact your organization’s efficiency, scalability, and bottom line. Whether you’re a large enterprise or a small business, there’s a server and infrastructure tier tailored to your needs. Choosing the right setup ensures you can harness the power of virtualization to drive your business forward. Remember, your choice should match your current workloads, future growth plans, and budget.
Many businesses struggle to find the right balance between performance and cost when investing in IT infrastructure. At PCSP, we provide a solution: high-quality refurbished servers and workstations backed by expert technical support. We help you overcome budget constraints and scale your capabilities with confidence.
Learn how you can reduce costs with PCSP — visit our website or contact us for a personalized consultation.
Shop Servers for Virtualization
HP Servers
- DL360 Gen9 – HSB 977355 – Virtualization Server - HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 8-Bay SFF - 2x Intel Xeon E5-2667 v4 (3.20GHz) 8C - 64GB DDR4 - 4x 512GB SSD - P440ar - 530T 10GbE RJ45 - Refurbished
- DL380 Gen10 – HSB 807976 – Virtualization Server - HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 8-Bay SFF - 2x Intel Xeon Gold 6136 (3.00GHz) 12C - 128GB DDR4 - 6x 512GB SSD - P408i-a - 560FLR-SFP+ 10GbE SFP+ - Refurbished
- DL360 Gen10 Plus – HSB 330773 – Virtualization Server - HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen10 Plus 10-Bay NVMe - 2x Intel Xeon Gold 6330 (2.00GHz) 28C - 256GB DDR4 - 4x 1.6TB NVMe U.2 SSD - MCX6314 10/25GbE SFP28 - Refurbished
Dell Servers
- R630 – DSB 906746 – Virtualization Server - Dell PowerEdge R630 8-Bay SFF - 2x Intel Xeon E5-2667 v4 (3.20GHz) 8C - 64GB DDR4 - 4x 512GB SSD - H730P - X540/I350 10GbE RJ45 - Refurbished
- R740 – DSB 678425 – Virtualization Server - Dell PowerEdge R740 8-Bay SFF - 2x Intel Xeon Gold 6154 (3.00GHz) 18C - 128GB DDR4 - 6x 512GB SSD - H740P - X520/I350 10GbE SFP+ - Refurbished
- R750 – DSB 078961 – Virtualization Server - Dell PowerEdge R750 8-Bay SFF Universal - 2x Intel Xeon Gold 6330 (2.00GHz) 28C - 256GB DDR4 - 4x 1.6TB NVMe U.2 SSD - H355/S150 - E810-XXV 10/25GbE SFP28 - Refurbished

